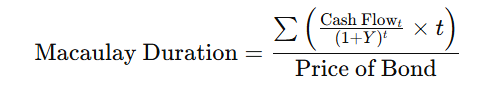Duration
Definition:
Duration is a financial measure that reflects the sensitivity of the price of a bond or other fixed-income security to changes in interest rates. It estimates the percentage change in the bond’s price for a 1% change in interest rates and helps investors gauge interest rate risk.
Key Points:
Measurement of Interest Rate Risk: Duration shows how much the price of a bond will change when interest rates fluctuate.
Time and Cash Flow Sensitivity: Bonds with longer maturities or deferred cash flows have higher durations.
Expressed in Years: It represents a weighted average time to receive all cash flows (coupon payments and principal repayment).
Types of Duration:
Macaulay Duration: Measures the weighted average time until cash flows are received, expressed in years.
Modified Duration: Adjusts Macaulay Duration to directly estimate the price sensitivity of a bond to changes in interest rates.
Formula:
Modified Duration = Macaulay Duration / (1 + (Yield/Number of Periods per Year))
Effective Duration: Used for bonds with embedded options (e.g., callable or puttable bonds) to account for cash flow uncertainty.
Formula for Macaulay Duration:
Where
t = Time period of each cash flow
Y = Yield to maturity (YTM)
Cash Flowt_t = Cash flow at time t
Example of Calculating Duration:
Scenario:
A bond has the following characteristics:
Face Value: $1,000
Annual Coupon Rate: 5%
Yield to Maturity (YTM): 4%
Maturity: 3 years
Steps:
Calculate the bond’s cash flows:
Year 1: $50 (coupon)
Year 2: $50 (coupon)
Year 3: $1,050 (coupon + principal repayment)
Discount each cash flow to present value (PV) using YTM:
PV= Cash Flow / (1+Y)^t
Year 1: 50 / (1.04)^1 = 48.08
Year 2: 50 / (1.04)^2 = 46.23
Year 3: 1050 / (1.04)^3 = 936.11
Compute the weighted average time:
Macaulay Duration = ((48.08 x 1) + (46.23 x 2) + 936.11 x 3)) / Bond Price
Assuming the bond price is the sum of discounted cash flows ($1,030.42):
Macaulay Duration = (48.08 + 92.46 + 2808.33) / 1030.42 = 2.89 years.
Modified Duration Example:
If the Macaulay Duration is 2.89 years and YTM is 4%, the Modified Duration is:
Modified Duration = 2.89 / 1 + 0.04 = 2.78
This indicates that for a 1% increase in interest rates, the bond’s price will decrease by approximately 2.78%.
Key Applications of Duration:
Portfolio Management: Helps investors manage interest rate risk and match liabilities with assets.
Bond Comparisons: Facilitates comparison of interest rate sensitivity across bonds with different maturities and cash flow structures.
Hedging Strategies: Assists in creating strategies to mitigate exposure to interest rate changes.
Factors Affecting Duration:
Time to Maturity: Longer maturities generally result in higher durations.
Coupon Rate: Higher coupon payments reduce duration because cash flows are received sooner.
Yield to Maturity (YTM): Higher yields reduce duration as discounted cash flows weigh less heavily in the average.
Conclusion:
Duration is a powerful tool for fixed-income investors to understand and manage interest rate risk. Whether planning for long-term goals or protecting against rate fluctuations, incorporating duration into decision-making helps ensure a balanced and resilient investment strategy.